

Steel Making starts with importing raw scrap from Middle East, Europe and USA.
The imported raw scrap is melted into steel. The Induction furnace is set at 1670 Degrees Celsius. Other elements are added to molten steel to obtain the required chemical composition as per standards. Upon satisfactory results after sample testing, the molten steel is poured into a ladle machine.
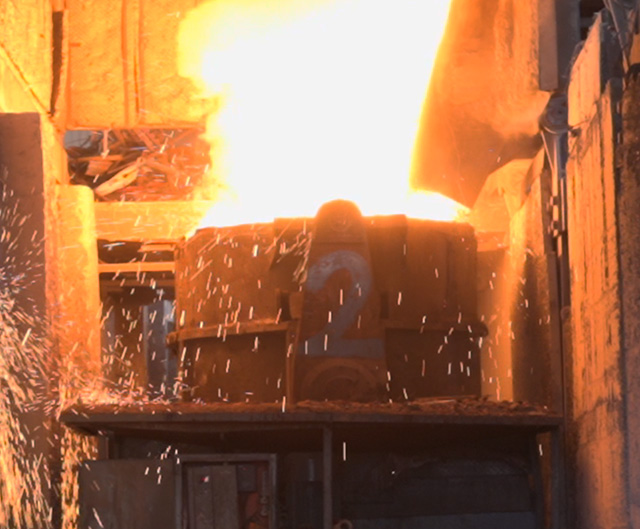
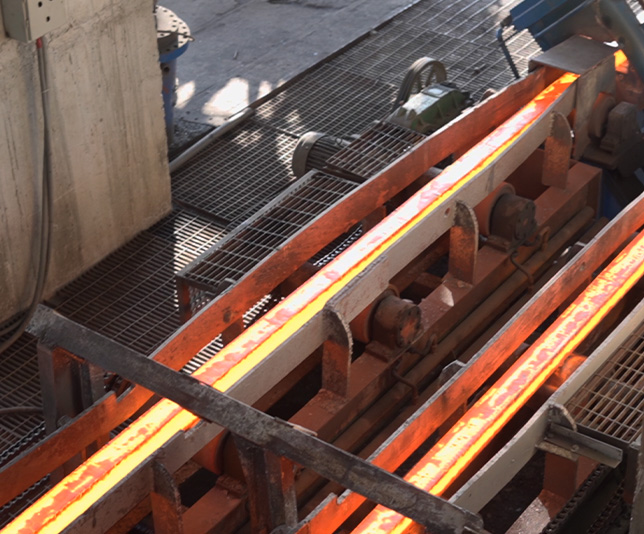


In the second step, the ladle carrying molten liquid is placed over a continuous casting machine (CCM). This machine solidifies molten steel into steel billets of desired sizes and widths.
In the second step, the ladle carrying molten liquid is placed over a continuous casting machine (CCM). This machine solidifies molten steel into steel billets of desired sizes and widths.

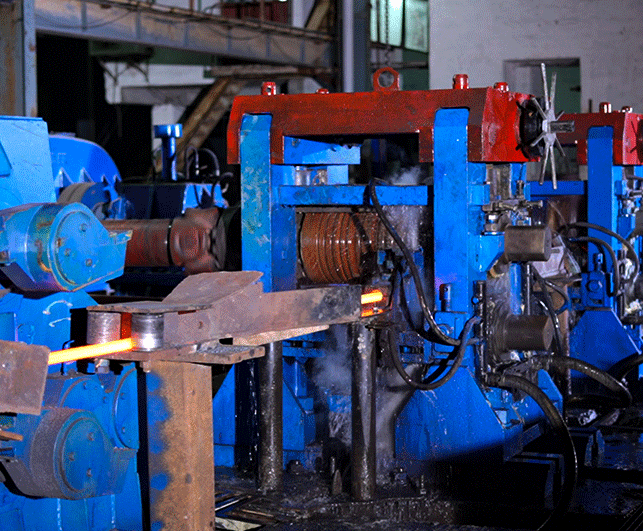
Steel Billets are directly fed into the Rolling Mill at 1OOO degrees Celsius. Rolling mill reduces the billet to the desired size of steel bars. The reduced steel bars are then thermo-mechanically-treated to achieve higher strength, ultimately reaching the cooling bed.
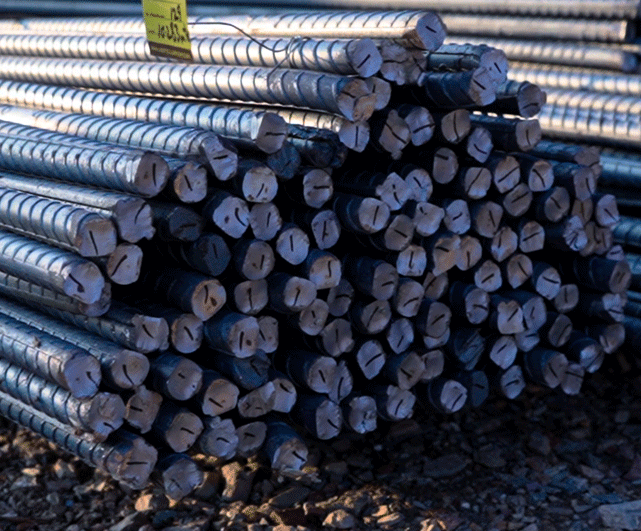

Samples of steel bars are drawn from the cooling bed for the mechanical testing lab. Upon satisfactory results, steel bars are tied in bundles with the tags of their respective batch properties.
Samples of steel bars are drawn from the cooling bed for the mechanical testing lab. Upon satisfactory results, steel bars are tied in bundles with the tags of their respective batch properties.
